1.概述
前段时间使用体验了ChatGPT的用法,感受到ChatGPT的强大,通过搜索关键字或者输入自己的意图,能够快速得到自己想要的信息和结果。今天笔者将深挖一下ChatGPT,给大家介绍如何使用ChatGPT的API来实战开发一些例子。
2.内容
2.1 ChatGPT起源
这个还得从谷歌发布BERT模型开始了解。BERT 是预训练语言表示法的一种方法。预训练涉及 BERT 如何首先针对大量文本进行训练,例如维基百科。然后,您可以将训练结果应用于其他自然语言处理 (NLP) 任务,例如问答系统和情感分析。借助 BERT 和 AI Platform Training,您可以在大约 30 分钟内训练各种 NLP 模型。
而OpenAI与BERT类似,做出了初代的GPT模型。它们的思想都是类似的,都是预计Transformer这种双向编码器,来获取文本内部的一些联系。
2.2 如何注册ChatGPT
由于OpenAI不允许国内手机注册申请账号,这里我们需要使用到虚拟手机号来注册接收信息(一次性购买使用),关于如果使用虚拟手机号,网上有很多资料和流程,这里就不细说了。大致流程如下:
- 准备一个邮箱,比如QQ邮箱、GMAIL等
- 访问OpenAI的官网地址
- 访问虚拟手机号网站,然后选择OpenAI购买虚拟机手机号(大概1块钱)
然后,注册成功后,我们就可以使用OpenAI的一些接口信息了。体验结果如下:

3.实战应用
3.1 数据集准备
在实战应用之前,我们需要准备好需要的数据集,我们可以从OpenAI的官网中通过Python API来生成模拟数据。具体安装命令如下所示:
pip install --upgrade openai
然后,我登录到OpenAI官网,申请一个密钥,用来获取一些训练所需要的数据。比如我们获取一个差评的代码实现如下:
import openaiimport timeimport pandas as pdimport numpy as npopenai.api_key = "<填写自己申请到的密钥地址>"completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="davinci", prompt="This hotel was terrible.",max_tokens=120)print("Terrible Comment:")print(completion.choices[0]['text'])
执行结果如下:

接着,我们来获取一个好评的代码例子,具体实现如下:
completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="davinci", prompt="This hotel was great.",max_tokens=120)print("Great Comment:")print(completion.choices[0]['text'])
执行结果如下:
现在,我们来获取所需要的数据集代码,具体实现如下所示:
print("Generating 500 good and bad reviews")good_reviews = []bad_reviews = []for i in range(0,500): completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="davinci", prompt="This hotel was great.",max_tokens=120) good_reviews.append(completion.choices[0]['text']) print('Generating good review number %i'%(i)) completion = openai.Completion.create(engine="davinci", prompt="This hotel was terrible.",max_tokens=120) bad_reviews.append(completion.choices[0]['text']) print('Generating bad review number %i'%(i)) display = np.random.choice([0,1],p=[0.7,0.3]) # 这里由于OpenAI的接口调用限制,控制一下循环调用频率 time.sleep(3) if display ==1: display_good = np.random.choice([0,1],p=[0.5,0.5]) if display_good ==1: print('Printing random good review') print(good_reviews[-1]) if display_good ==0: print('Printing random bad review') print(bad_reviews[-1])# Create a dataframe with the reviews and sentimentdf = pd.DataFrame(np.zeros((1000,2)))# Set the first 500 rows to good reviewsdf.columns = ['Reviews','Sentiment']df['Sentiment'].loc[0:499] = 1df['Reviews'] = good_reviews+bad_reviews# Export the dataframe to a csv filedf.to_csv('generated_reviews.csv')
执行结果如下:
3.2 开始进行算法训练
有了数据之后,我们可以建立和训练一种机器学习算法,当我们处理文本的时候,首先需要做的是使用矢量器,矢量器是将文本转换为矢量的东西。相似的的文本有着相似的向量,不同的文本具有不相似的向量。
而矢量化的步骤有很多方法可以实现,为了实现文本中的功能,我们借助Python的TFIDF矢量器的库来实现。
具体实现代码如下所示:
import pandas as pd import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,plot_confusion_matrixfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer# Split the data into training and testinglabeled_data = pd.read_csv('generated_reviews.csv').drop(columns=['Unnamed: 0'])labeled_data.Sentiment = labeled_data.Sentiment.astype(int)labeled_data = labeled_data.dropna().reset_index()# print head of the dataprint(labeled_data.head())
头部数据结果如下所示:
接着,我们对数据进行矢量化,具体实现代码如下所示:
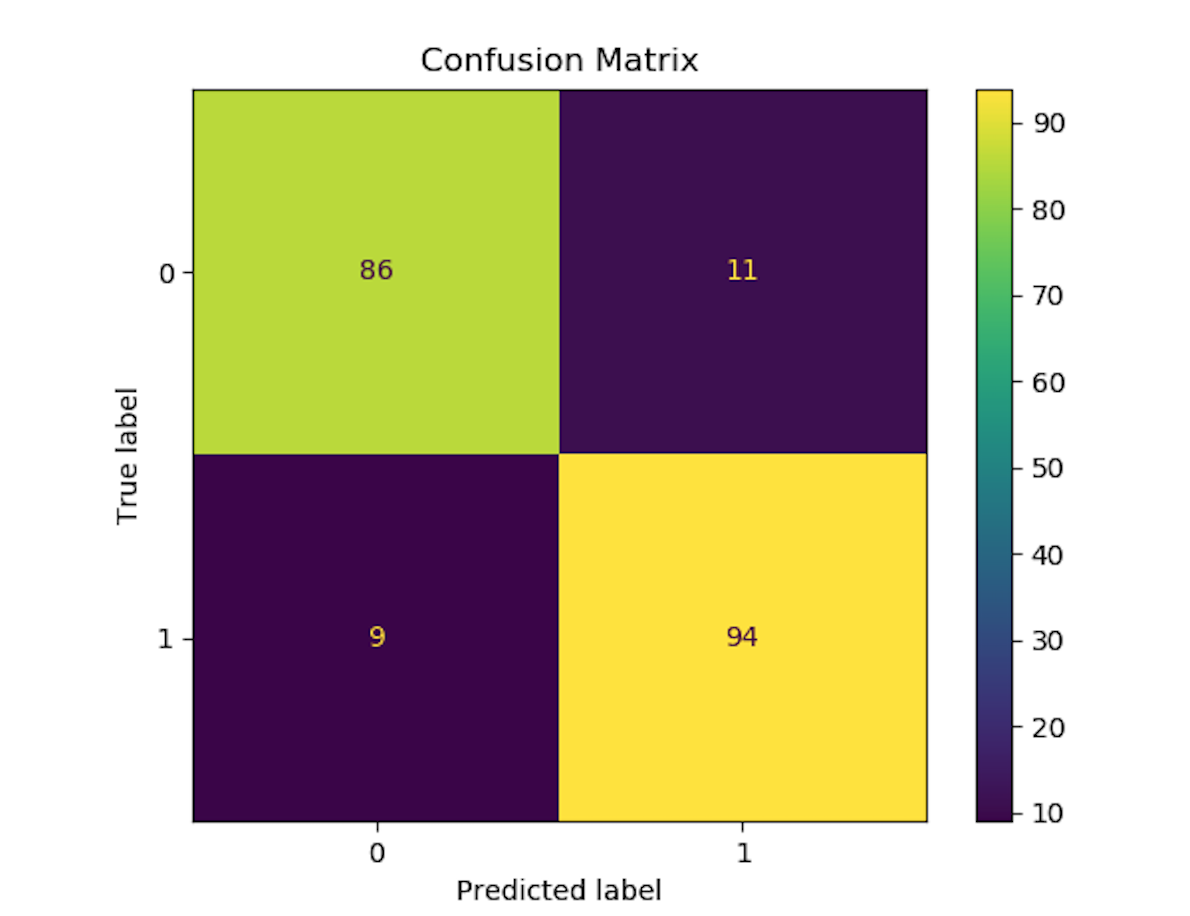
dataset = labeled_datavectorizer = TfidfVectorizer (max_features=2500, min_df=7, max_df=0.8)tokenized_data = vectorizer.fit_transform(dataset['Reviews']).toarray()labels = np.array(dataset["Sentiment"]) # Label is already an array of 0 and 1rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)X = tokenized_datay = labelsX_train, X_test,y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y,test_size=0.2)rf.fit(X_train,y_train)plot_confusion_matrix(rf,X_test,y_test)# save the result to diskplt.title('Confusion Matrix')plt.savefig('result.png')
这里涉及到使用随机森林的模型,随机森林是一种有监督的机器学习算法。由于其准确性,简单性和灵活性,它已成为最常用的一种算法。事实上,它可以用于分类和回归任务,再加上其非线性特性,使其能够高度适应各种数据和情况。
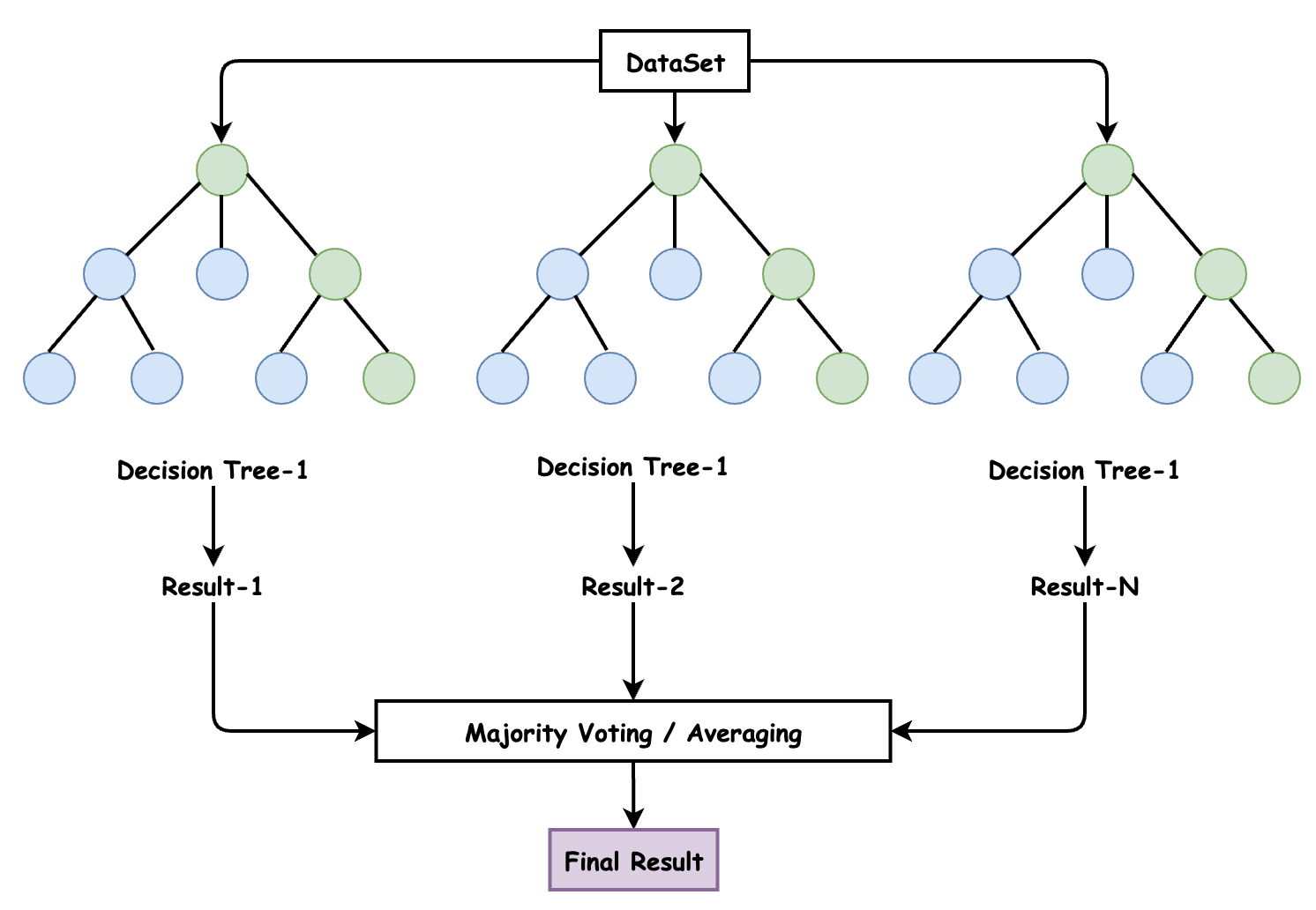
它之所以被称为 “森林”,是因为它生成了决策树森林。然后,来自这些树的数据合并在一起,以确保最准确的预测。虽然单独的决策树只有一个结果和范围狭窄的群组,但森林可以确保有更多的小组和决策,从而获得更准确的结果。它还有一个好处,那就是通过在随机特征子集中找到最佳特征来为模型添加随机性。总体而言,这些优势创造了一个具有广泛多样性的模型。
我们执行这个模型,然后输出结果如下图所示:
4.总结
OpenAI API 几乎可以应用于任何涉及理解或生成自然语言或代码的任务。它提供一系列具有不同功率级别的模型,适用于不同的任务,并且能够微调您自己的自定义模型。这些模型可用于从内容生成到语义搜索和分类的所有领域。



